The Ford Crown Victoria P71, also commonly known as the “Crown Vic,” is a venerable sedan that has earned its reputation primarily as a police and fleet vehicle. Introduced by Ford Motor Company, the Crown Victoria P71 embodies durability, reliability, and robustness. Known for its spacious interior, powerful V8 engine, and rear-wheel-drive layout, it has been the vehicle of choice for many law enforcement agencies across the United States. This model, the 2004 Crown Victoria P71, continues the legacy with enhancements in power and performance and is especially notable for its longevity, often surpassing hundreds of thousands of miles in service with minimal maintenance. Lets find out Which Spark Plugs for 2004 Crown Victoria P71.

History and Significance of Ford Crown Victoria P71
The Ford Crown Victoria P71 has a rich history and significance ingrained in American automotive culture. Introduced in the mid-1990s as a part of Ford’s Panther platform, it quickly became synonymous with law enforcement and taxi services, owing to its sturdy construction, powerful engine, and ease of maintenance. The “P71” designation refers to Ford’s police package, distinguished by its enhancements for heavy-duty use, including an improved suspension, cooling, and electrical system.
Over the years, the Crown Vic, especially the 2004 model, has gained a cult following among car enthusiasts and collectors. Its significance lies not just in its ubiquitous presence on American roads, but also in its portrayal in numerous films and television series, further cementing its iconic status. Despite ceasing production in 2011, the Crown Victoria P71 symbolizes American resilience, reliability, and functional design.
Performance Specifications
The 2004 Crown Victoria P71 is powered by a 4.6-liter V8 engine that delivers 250 horsepower and 297 lb-ft of torque. This robust engine is paired with a 4-speed automatic transmission that provides smooth and responsive gear changes. For a vehicle of its size, the Crown Vic P71 offers remarkable acceleration and power, reaching 0 to 60 mph in just 8.1 seconds.
The car’s fuel economy is relatively modest, with an EPA rating of 14 mpg in the city and 21 mpg on the highway. However, this is understandable considering its high-performance nature and the heavy-duty usage it’s designed for. The Crown Vic P71 is also renowned for its impressive handling capabilities, thanks to its rear-wheel-drive layout and sturdy suspension. Its braking system is robust and reliable, ensuring safety in high-speed pursuits or emergency situations.
Overall, the 2004 Crown Victoria P71 delivers a well-rounded performance package, making it a reliable choice for fleet and personal use. Despite its age, this vehicle still holds its own in terms of power, speed, and durability, a testament to its timeless design and engineering.

Importance of Quality Spark Plugs
Fuel Efficiency
The condition and quality of the spark plugs can significantly impact the fuel efficiency of the 2004 Crown Victoria P71. These small yet integral components of the vehicle’s ignition system are crucial in ensuring optimal fuel combustion. By generating a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s combustion chamber, spark plugs facilitate the vehicle’s smooth operation.
When these sparks are consistent and at the right timing, the engine runs more efficiently, enhancing fuel economy. Over time, however, spark plugs can wear down or accumulate deposits, leading to less efficient ignition and, consequently, reduced fuel efficiency. Regular inspection and timely replacement of spark plugs contribute to maintaining and, in some cases, improving the fuel efficiency of your 2004 Crown Victoria P71.
Engine Longevity
The longevity of the 2004 Crown Victoria P71’s engine is another aspect significantly influenced by the state of the spark plugs. A well-functioning spark plug ensures a clean and robust combustion process, lessening the overall strain on the engine. This extends the engine lifespan, allowing it to maintain optimal performance even over high mileage. Conversely, damaged or worn-out spark plugs can lead to problems such as misfires, hard starting, and engine surges or hesitations, which can result in serious engine damage over time. Therefore, regular spark plug maintenance is an essential preventative measure that can help prolong the life of your Crown Victoria P71’s high-performance engine.

Top Brands for Crown Victoria P71 Spark Plugs
When selecting spark plugs for your 2004 Crown Victoria P71, it’s crucial to choose a product that matches the quality and durability of your vehicle. Here are the top brands that offer high-quality spark plugs:
1. Motorcraft: As Ford’s official parts brand, Motorcraft spark plugs are a reliable choice for your Crown Victoria P71. They are designed to meet Ford’s performance standards and are often the brand installed in the vehicle at the factory.
2. NGK: Known for their superior quality and durability, NGK spark plugs are popular among car enthusiasts and professionals. They offer excellent heat dissipation and strong performance, ensuring optimal engine efficiency.
3. Bosch: Offering an array of spark plug options, Bosch is recognized for its innovation and quality. Their spark plugs are designed to provide reliable sparking, enhancing fuel efficiency and engine performance.
4. Denso: With a reputation for resilience and reliability, Denso spark plugs are an excellent choice for extending engine life and improving overall vehicle performance. They are designed to resist wear and tear, ensuring a longer service life.
5. ACDelco: A trusted name in automotive parts, ACDelco offers high-quality spark plugs that provide reliable ignition and optimal fuel economy. They are engineered to withstand the rigors of high-performance engines like the one in your Crown Victoria P71.
Remember, while these brands are renowned for their quality, choosing a spark plug that matches your vehicle’s specific requirements is essential for the best results. Refer to your vehicle’s owner manual or consult a professional mechanic when selecting new spark plugs.
Don’t miss our comprehensive guide, “Best Spark Plugs for P71: Reviews, Guide,” to discover the top spark plugs for your P71. Check it out now!
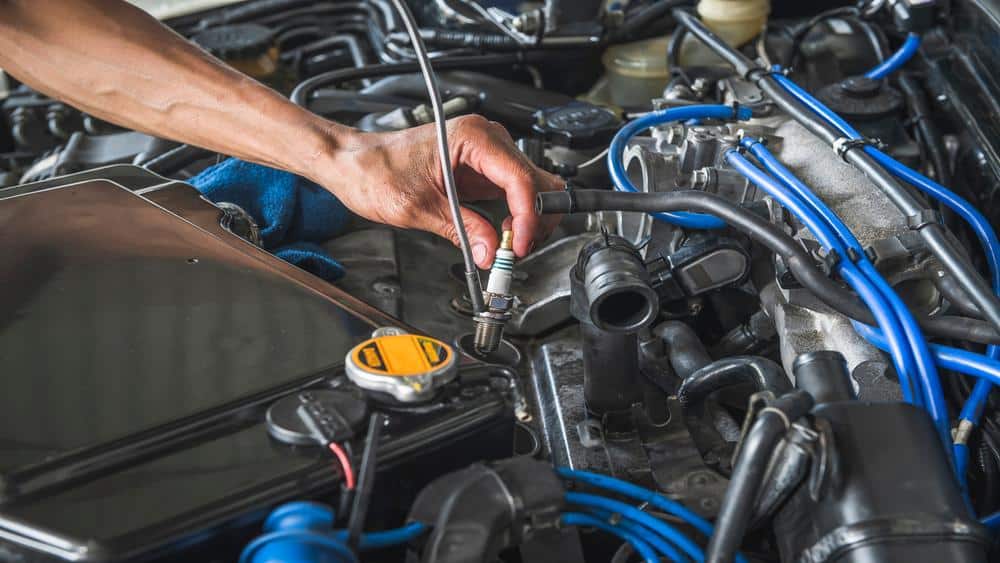

How to Install Spark Plugs in your Crown Victoria P71
Tools Needed
Before we begin installing spark plugs in your 2004 Crown Victoria P71, it is essential to ensure you have the necessary tools handy. Here’s the list of tools you will need:
- Spark plug socket: This type of socket is designed to install and remove spark plugs without causing any damage.
- Ratchet: You’ll need a ratchet to turn the spark plug socket.
- Extension bars: These will help you reach the deep spark plugs within the engine compartment.
- Spark plug gap tool: This tool is needed to check and adjust the new spark plugs’ gap per the vehicle’s specifications.
- Torque wrench: This tool is optional but recommended for tightening the spark plugs to the correct torque specification.
- Wire brush or spray-on plug cleaner: This helps clean the threads in the spark plug hole, if necessary.
- Anti-seize compound: This is applied to the threads of the new spark plugs to prevent them from seizing in the cylinder head.
- Dielectric grease: This is used to lubricate the inside of the spark plug wire boots to prevent sticking and corrosion.
Remember, each vehicle may have slight variations in the tools required for spark plug replacement. Always refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the most accurate information.
Step-by-Step Guide
Follow the steps below to replace the spark plugs in your 2004 Crown Victoria P71:
- Prepare the Vehicle: Start by ensuring the vehicle is turned off and cooled down to avoid burns from a hot engine. Open the hood and locate the spark plug wires. They are typically thick wires running from the ignition coil to the top of the engine.
- Remove the Spark Plug Wire: Grasp the boot (the thicker part) of the first spark plug wire and gently twist it to loosen the seal. Pull the boot off the spark plug. Avoid pulling on the wire itself, as this can cause damage.
- Remove the Old Spark Plug: Attach the spark plug socket to your ratchet. Use an extension bar if necessary. Insert the socket over the spark plug and turn the ratchet counterclockwise to loosen and remove the spark plug.
- Prepare the New Spark Plug: Use the spark plug gap tool to adjust the gap on your new spark plug to the vehicle’s specifications. Apply a small amount of anti-seize compound to the threads of the new spark plug.
- Install the New Spark Plug: Insert the new spark plug into the spark plug hole. Use the spark plug socket and ratchet (without the extension bar) to tighten it by hand. Once the spark plug is snug, use a torque wrench to tighten it to the correct torque specification.
- Reattach the Spark Plug Wire: Apply a small amount of dielectric grease inside the boot of the spark plug wire. Push the boot onto the new spark plug until it clicks into place.
- Repeat for Remaining Spark Plugs: Follow the same process to replace the remaining spark plugs.
- Final Check: Once all spark plugs are replaced, make a final check to ensure all wires are correctly attached, and all tools are removed from the engine area.
- Test Drive: Start the vehicle and take a short test drive to ensure everything runs smoothly. Pay attention to the engine’s performance and note any irregularities.
Always remember to dispose of your old spark plugs responsibly and consider recycling them if this service is available in your area. Regular spark plug maintenance can significantly improve the performance and lifespan of your vehicle.
Precautions
When replacing spark plugs, it’s crucial to take certain safety precautions to protect yourself and your vehicle:
- Avoid working on a hot engine: Always ensure your vehicle has had ample time to cool before starting the process. A hot engine can cause severe burns.
- Properly gap your spark plugs: Incorrectly gapped spark plugs can lead to poor performance and potential engine damage. Always check and adjust the gap before installation.
- Do not over-tighten spark plugs: Over-tightening can damage the spark plug or even the cylinder head. Utilize a torque wrench for accurate tightening.
- Avoid cross-threading: Cross-threading occurs when a spark plug is not correctly aligned with the spark plug hole. If this happens, it can damage the threads in the cylinder head, leading to costly repairs.
- Use anti-seize sparingly: While anti-seize prevents spark plugs from getting stuck in the cylinder head, too much can lead to over-tightening. A small amount on the threads is sufficient.
- Don’t force the spark plug wires: When reattaching the spark plug wires, never force them on. If they do not easily slide onto the spark plug, an issue may need to be addressed.
- Always wear safety glasses: Protect your eyes from potential debris by wearing safety glasses while operating under the hood.
Remember, if you need help performing this maintenance yourself, it’s always best to seek the help of a professional mechanic.
Tips for a Smooth Process
When replacing spark plugs, following these tips can help ensure a smooth and efficient process:
- Organize Your Tools: Before you start, have all your tools within reach. This will help you stay organized and save time during the replacement process.
- Clean Your Workspace: Ensure the engine and surrounding areas are clean. This will prevent debris from falling into the cylinder when removing the spark plug.
- Work on One Plug At A Time: To avoid mixing up the spark plug wires, replace one at a time. This will also prevent debris from entering open spark plug holes.
- Inspect Your Spark Plugs: Use this opportunity to inspect your old spark plugs. The condition of your old spark plugs can tell you a lot about the engine’s condition. For example, oil or soot on the spark plug can indicate a bigger issue that may need to be examined.
- Remember the Order: Pay attention to the order in which the spark plug wires are attached. They need to be reattached in the same order.
- Ask for Help if Needed: Feel free to consult a professional if you need clarification on any step in the process. It’s better to ask for help than to risk damaging your vehicle.
Following these tips can make the spark plug replacement process easier and more efficient. Always remember that safety is paramount when working on your vehicle.
Conclusion & Recommendations
Replacement of spark plugs is a common maintenance task that can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your vehicle. Although the process may seem complex, with the right tools and a methodical approach, it can be undertaken by vehicle owners with a basic understanding of car mechanics.
However, it’s essential to remember that every vehicle is different, and the specifics of this task can vary based on your car’s make, model, and year. Always consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for precise instructions and specifications.
Feel free to seek professional assistance if you’re ever in doubt or uncomfortable performing this task. A professional mechanic can quickly and accurately complete this task, saving you from potential errors that could lead to more significant problems.
In conclusion, regular maintenance, including spark plug replacement, is crucial for the overall health of your vehicle. Follow the tips and precautions above, stay organized, and never rush the process. Remember, patience and meticulousness will lead to the best results. Your vehicle and wallet will thank you in the long run.